Foot Bunions And Corns
Overview
 A bunion, (medical term: hallux abductovalgus) is a condition resulting in boney prominence at the inside of the foot at the big toe joint. A bunion occurs when the big toe begins to deviate toward the second toe. The biggest misconception is that bunions occur from an overgrowth of bone. While that may be true in very few people, the bunion really represents a dislocation of the big toe joint as it bulges against the skin.
A bunion, (medical term: hallux abductovalgus) is a condition resulting in boney prominence at the inside of the foot at the big toe joint. A bunion occurs when the big toe begins to deviate toward the second toe. The biggest misconception is that bunions occur from an overgrowth of bone. While that may be true in very few people, the bunion really represents a dislocation of the big toe joint as it bulges against the skin.
Causes
Women traditionally have a higher rate of bunions, which is to be expected, since it is they who have traditionally worn shoes with high heels, a narrow toe box, or whatever fashion dictates from year to year. However, men can suffer from bunions as well, as can anyone for whom the right (or wrong) conditions exist, poor foot mechanics, improper footwear, occupational hazards, health and genetic predisposition. Finally, bunions have long been a condition associated with the elderly, and although they often appear in conjunction with inflammatory joint diseases such as arthritis (which is often associated with age), they can strike at any point in life, including adolescence.
Symptoms
Symptoms, which occur at the site of the bunion, may include pain or soreness, inflammation and redness, a burning sensation, possible numbness. Symptoms occur most often when wearing shoes that crowd the toes, such as shoes with a tight toe box or high heels. This may explain why women are more likely to have symptoms than men. In addition, spending long periods of time on your feet can aggravate the symptoms of bunions.
Diagnosis
A simple visual exam is all it will take for your doctor to determine whether you have a bunion. He or she may also ask you to move your big toe in order to ascertain your range of motion. Your doctor may also look for any inflammation, redness, or pain. X-rays can help your doctor determine the severity and cause of the bunion. Your doctor may also ask you questions about your footwear, the symptoms you are experiencing, and if other family members also suffer from the condition. All these factors will help him or her diagnose you properly.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment falls into two broad categories, conservative and surgical. From a conservative standpoint, efforts are directed at correcting faulty foot mechanics with custom molded insoles and relief of symptoms. These include Custom Orthosis to stabilize the abnormal motion of the hind and fore foot. Shoe gear modification: Using shoes with larger toe boxed and more supple materials. Changes in activities. Try to avoid those things which cause symptoms. Anti-inflammatory medication for periodic relief this includes cortisone injections into the joint as well as oral medication. 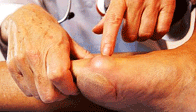
Surgical Treatment
Bunion surgery is most often a day case or one night in hospital. Surgery can be done under ankle block (patient awake) or general anaesthetic. It is best to rest with the foot elevated for the first 2 weeks after surgery. The foot is bandaged and a special sandal supplied by the hospital is worn for 6 weeks. Sensible shoes are to be worn for a further 6 weeks after the bandages are removed. It will take between 3-6 months for the swelling to go down. It will take 12 months before everything completely settles. It is also important to remember that not all bunion operations are entirely successful.
Overpronation Of The Feet
Pronation occurs as weight is transferred from the heel to the forefoot and the foot rolls inwards. Or to put it a little more technically; pronation is the movement of the subtalar joint (between the talus and calcaneus) into eversion, dorsi flexion and abduction (turning the sole outwards, upwards and sideways). A certain amount of this is natural but it many people the foot rolls in too much or over pronates.

Causes
Generally fallen arches are a condition inherited from one or both parents. In addition, age, obesity, and pregnancy cause our arches to collapse. Being in a job that requires long hours of standing and/or walking (e.g. teaching, retail, hospitality, building etc) contributes to this condition, especially when standing on hard surfaces like concrete floors. Last, but not least unsupportive footwear makes our feet roll in more than they should.
Symptoms
Overpronation can be a contributing factor in other lower extremity disorders, such as foot pain, plantar fasciitis, ankle injuries, medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints), periostitis, stress fractures and myofascial trigger points. Overpronation increases the degree of internal tibial rotation, thereby contributing to various knee disorders such as meniscal injury or ligament sprains. The effects of the postural deviation are exaggerated in athletes due to the increase in foot strikes while running and the greater impact load experienced. When running, three to four times the body weight is experienced with each foot strike.2 If overpronation exists, the shock force is not adequately absorbed by the foot and is transmitted further up the kinetic chain.
Diagnosis
Pronounced wear on the instep side of shoe heels can indicate overpronation, however it's best to get an accurate assessment. Footbalance retailers offer a free foot analysis to check for overpronation and help you learn more about your feet.

Non Surgical Treatment
The way a foot orthotic works is by altering the weight-bearing surface of the foot. The simulated foot improvement is only possible when standing still with full weight applied. Orthotics are of little help through most of the actual walking cycle. observationPatients may experience some symptom relief, but the orthotic cannot correct the internal osseous misalignment. Over-the-counter foot orthotics are usually of little help and wear out quickly. Custom-made foot orthotics, obtained through your doctor's office, are generally expensive. Though they last longer and have less chance of ill-effects than OTC brands, they still need to be replaced often. Over a lifetime, an individual can spend several thousands of dollars in total costs associated with orthotics and see little or no results. This is because orthotics only work when you are wearing them and do not treat the cause of the problem. In many cases, the external pressure points created by orthotics can cause more problems than solutions. Blisters, sore feet, sore joints and many other long-term complications can arise as a consequence of wearing orthotics.
Surgical Treatment
The MBA implant is small titanium device that is inserted surgically into a small opening between the bones in the hind-mid foot: the talus (ankle bone) and the calcaneus (heel bone). The implant was developed to help restore the arch by acting as a mechanical block that prevents the foot from rolling-in (pronation). In the medical literature, the success rate for relief of pain is about 65-70%. Unfortunately, about 40% of people require surgical removal of the implant due to pain.
What Would Cause Calcaneal Apophysitis?
Sever's Disease, otherwise known as calcaneal apophysitis is an inflammation of the growth plate in the heel of growing children, typically adolescents. The condition presents as pain in the heel and is caused by repetitive stress to the heel and is thus particularly common in active children. It usually resolves once the bone has completed growth or activity is lessened.
Causes
Sever?s disease is most likely to occur during the growth spurt that occurs in adolescence. For girls, growth spurts usually occurs between 8 and 13 years of age. For boys, it?s typically between 10 and 15 years of age. The back of the heel hardens and becomes stronger when it finishes growing, which is why Sever?s rarely occurs in older adolescents and teenagers.
Symptoms
Pain in the bottom surface and at the back of the heel. Extreme pain when the child places their heel on the ground. The pain is aggravated when running or jumping on hard surfaces. The pain is reduced when the child walks or runs on their toes.
Diagnosis
In Sever's disease, heel pain can be in one or both heels. It usually starts after a child begins a new sports season or a new sport. Your child may walk with a limp. The pain may increase when he or she runs or jumps. He or she may have a tendency to tiptoe. Your child's heel may hurt if you squeeze both sides toward the very back. This is called the squeeze test. Your doctor may also find that your child's heel tendons have become tight.
Non Surgical Treatment
The primary method of treating Sever?s disease is taking time off from sports and other physical activities to alleviate the pressure on the heel bone. During the healing period, your child?s doctor may also recommend physical therapy or any type of exercise that involves stretching and strengthen leg muscles and tendons. Wrapping ice in a towel and placing it under the child?s heel will also help to alleviate and reduce pain and swelling.
Prevention
Treat symptoms when they occur with RICE and NO HARM. RICE (Rest Ice, Compression and Elevation) will help following activity and when symptoms flare, while No HARM (No Heat, alcohol, running or massage) will help reduce the symptoms from occurring. Orthotics. The use of an Interpod Orthotic will assist in realigning the foot, which will reduce the stress on the Achilles Tendon and prevent reoccurring symptoms. The orthotic achieves this by reducing the forces and stress placed on the limbs during walking and running. Exercise reduction. Patients may need to reduce their level of activity if this is seen as a contributing factor. Training errors. Ensue athletes warm up and cool down correctly with stretching activities. Footwear. Sporting and school shoes should have an appropriate heel height to assist in offloading of the Achilles tendon.
Partial Achilles Tendon Rupture Recovery
Overview
 The Achilles tendon is the tough sinew that attaches the calf muscle to the back of the calcaneus, or heel bone. It is also known as the tendo calcaneus or the tendo Achilles and happens to be one of the longest tendons in the body. An Achilles tendon rupture occurs when the Achilles tendon is partially or completely broken or torn. The average age of patients who suffer Achilles tendon ruptures is 30 to 40 years. The male-to-female ratio is nearly 20 to 1.
The Achilles tendon is the tough sinew that attaches the calf muscle to the back of the calcaneus, or heel bone. It is also known as the tendo calcaneus or the tendo Achilles and happens to be one of the longest tendons in the body. An Achilles tendon rupture occurs when the Achilles tendon is partially or completely broken or torn. The average age of patients who suffer Achilles tendon ruptures is 30 to 40 years. The male-to-female ratio is nearly 20 to 1.
Causes
People who commonly fall victim to Achilles rupture or tear include recreational athletes, people of old age, individuals with previous Achilles tendon tears or ruptures, previous tendon injections or quinolone use, extreme changes in training intensity or activity level, and participation in a new activity. Most cases of Achilles tendon rupture are traumatic sports injuries. The average age of patients is 29-40 years with a male-to-female ratio of nearly 20:1. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin, and glucocorticoids have been linked with an increased risk of Achilles tendon rupture. Direct steroid injections into the tendon have also been linked to rupture. Quinolone has been associated with Achilles tendinitis and Achilles tendon ruptures for some time. Quinolones are antibacterial agents that act at the level of DNA by inhibiting DNA Gyrase. DNA Gyrase is an enzyme used to unwind double stranded DNA which is essential to DNA Replication. Quinolone is specialized in the fact that it can attack bacterial DNA and prevent them from replicating by this process, and are frequently prescribed to the elderly. Approximately 2% to 6% of all elderly people over the age of 60 who have had Achilles ruptures can be attributed to the use of quinolones.
Symptoms
The classic sign of an Achilles' tendon rupture is a short sharp pain in the Achilles' area, which is sometimes accompanied by a snapping sound as the tendon ruptures. The pain usually subsides relatively quickly into an aching sensation. Other signs that are likely to be present subsequent to a rupture are the inability to stand on tiptoe, inability to push the foot off the ground properly resulting in a flat footed walk. With complete tears it may be possible to feel the two ends of tendon where it has snapped, however swelling to the area may mean this is impossible.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Achilles tendon rupture is not difficult. Usually, the diagnosis is obvious after examination of the ankle and performing some easy foot maneuvers (such as attempting to stand on the toes). When an Achilles tendon rupture occurs, there is often clinical confirmation of tenderness and bruising around the heel. A gap is felt when the finger is passed over the heel area, where the rupture has developed. All individuals with a full-blown rupture of the tendon are unable to stand on their toes. There is no blood work required in making a diagnosis of Achilles tendon rupture. The following are three common radiological tests to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendon rupture. Plain X-rays of the foot may reveal swelling of the soft tissues around the ankle, other bone injury, or tendon calcification. Ultrasound is the next most commonly ordered test to document the injury and size of the tear. For a partial tear of the Achilles tendon, the diagnosis is not always obvious on a physical exam and hence an ultrasound is ordered. This painless procedure can make a diagnosis of partial/full Achilles tendon rupture rapidly. Ultrasound is a relatively inexpensive, fast, and reliable test. MRI is often ordered when diagnosis of tendon rupture is not obvious on ultrasound or a complex injury is suspected. MRI is an excellent imaging test to assess for presence of any soft-tissue trauma or fluid collection. More importantly, MRI can help detect presence of tendon thickening, bursitis, and partial tendon rupture. However, MRI is expensive and is not useful if there is any bone damage.
Non Surgical Treatment
Nonsurgical method is generally undertaken in individuals who are old, inactive, and at high-risk for surgery. Other individuals who should not undergo surgery are those who have a wound infection/ulcer around the heel area. A large group of patients who may not be candidates for surgery include those with diabetes, those with poor blood supply to the foot, patients with nerve problems in the foot, and those who may not comply with rehabilitation. Nonsurgical management involves application of a short leg cast to the affected leg, with the ankle in a slightly flexed position. Maintaining the ankle in this position helps appose the tendons and improves healing. The leg is placed in a cast for six to 10 weeks and no movement of the ankle is allowed. Walking is allowed on the cast after a period of four to six weeks. When the cast is removed, a small heel lift is inserted in the shoe to permit better support for the ankle for an additional two to four weeks. Following this, physical therapy is recommended. The advantages of a nonsurgical approach are no risk of a wound infection or breakdown of skin and no risk of nerve injury. The disadvantages of the nonsurgical approach includes a slightly higher risk of Achilles tendon rupture and the surgery is much more complex if indeed a repair is necessary in future. In addition, the recuperative period after the nonsurgical approach is more prolonged. 
Surgical Treatment
The best treatment for a ruptured Achilles tendon in an active individual is typically surgery. While an Achilles rupture can sometimes be treated with a cast, splint, brace, or other device that will keep your lower leg from moving, surgery provides less chance that the tendon will rupture again and offers more strength and a shorter recovery period. Surgery may be delayed for a period of a week after the rupture, to let the swelling go down. There are two types of surgery to repair a ruptured Achilles tendon and both involve the surgeon sewing the tendon back together through the incision. Open surgery, the surgeon makes a single large incision in the back of the leg. Percutaneous surgery, the surgeon makes a number of small incisions rather than one large incision. Depending on the condition of the torn tissue, the repair may be reinforced with other tendons.
Functional Leg Length Discrepancy Heel Lift
Surgical lengthening of the shorter extremity (upper or lower) is another treatment option. The bone is lengthened by surgically applying an external fixator to the extremity in the operating room. The external fixator, a scaffold-like frame, is connected to the bone with wires, pins or both. A small crack is made in the bone and tension is created by the frame when it is "distracted" by the patient or family member who turns an affixed dial several times daily. The lengthening process begins approximately five to ten days after surgery. The bone may lengthen one millimeter per day, or approximately one inch per month. Lengthening may be slower in adults overall and in a bone that has been previously injured or undergone prior surgery. Bones in patients with potential blood vessel abnormalities (i.e., cigarette smokers) may also lengthen more slowly. The external fixator is worn until the bone is strong enough to support the patient safely, approximately three months per inch of lengthening. This may vary, however, due to factors such as age, health, smoking, participation in rehabilitation, etc. Risks of this procedure include infection at the site of wires and pins, stiffness of the adjacent joints and slight over or under correction of the bone?s length. Lengthening requires regular follow up visits to the physician?s office, meticulous hygiene of the pins and wires, diligent adjustment of the frame several times daily and rehabilitation as prescribed by your physician.

Causes
The causes of LLD may be divided into those that shorten a limb versus those that lengthen a limb, or they may be classified as affecting the length versus the rate of growth in a limb. For example, a fracture that heals poorly may shorten a leg slightly, but does not affect its growth rate. Radiation, on the other hand, can affect a leg's long-term ability to expand, but does not acutely affect its length. Causes that shorten the leg are more common than those that lengthen it and include congenital growth deficiencies (seen in hemiatrophy and skeletal dysplasias ), infections that infiltrate the epiphysis (e.g. osteomyelitis ), tumors, fractures that occur through the growth plate or have overriding ends, Legg-Calve-Perthes disease, slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE), and radiation. Lengthening can result from unique conditions, such as hemihypertrophy , in which one or more structures on one side of the body become larger than the other side, vascular malformations or tumors (such as hemangioma ), which cause blood flow on one side to exceed that of the other, Wilm's tumor (of the kidney), septic arthritis, healed fractures, or orthopaedic surgery. Leg length discrepancy may arise from a problem in almost any portion of the femur or tibia. For example, fractures can occur at virtually all levels of the two bones. Fractures or other problems of the fibula do not lead to LLD, as long as the more central, weight-bearing tibia is unaffected. Because many cases of LLD are due to decreased rate of growth, the femoral or tibial epiphyses are commonly affected regions.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of all forms of LLD is chronic backache. In structural LLD the sufferer may also experience arthritis within the knee and hip are, flank pain, plantar fasciitis and metatarsalgia all on the side that is longer. Functional LLD sufferers will see similar conditions on the shorter side.
Diagnosis
On standing examination one iliac crest may be higher/lower than the other. However a physiotherapist, osteopath or chiropractor will examine the LLD in prone or supine position and measure it, confirming the diagnosis of structural (or functional) LLD. The LLD should be measured using bony fixed points. X-Ray should be taken in a standing position. The osteopath, physiotherapist or chiropractor will look at femoral head & acetabulum, knee joints, ankle joints.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of leg length inequality involves many different approaches, such as orthotics, epiphysiodesis, shortening, and lengthening, which can be used alone or combined in an effort to achieve equalization of leg lengths. Leg length inequality of 2 cm or less is usually not a functional problem. Often, leg length can be equalized with a shoe lift, which usually corrects about two thirds of the leg length inequality. Up to 1 cm can be inserted in the shoe. For larger leg length inequalities, the shoe must be built up. This needs to be done for every shoe worn, thus limiting the type of shoe that the patient can wear. Leg length inequalities beyond 5 cm are difficult to treat with a shoe lift. The shoe looks unsightly, and often the patient complains of instability with such a large lift. A foot-in-foot prosthesis can be used for larger leg length inequalities. This is often done as a temporizing measure for young children with significant leg length inequalities. The prosthesis is bulky, and a fixed equinus contracture may result.

Surgical Treatment
Surgeries to lengthen a leg are generally only performed when there is a difference in leg length of greater than four centimeters. These types of surgeries can be more difficult and have more complications, such as infections, delayed healing, dislocations, and high blood pressure. In a several step process, bone lengthening surgeries involve cutting a bone in two in order to allow new bone growth to occur. After the bone is cut, a special apparatus is worn with pins that will pull the bone apart at approximately one millimeter per day. This causes osteogenesis, or new bone growth, in between the cut bone segments. A cast or brace may be required for several months after surgery to allow the new bone growth to harden and provide extra support.
Can You Correct Flat Feet In Adults?
Overview
Adult flatfoot refers to a deformity that develops after skeletal maturity is reached. Adult flatfoot should be differentiated from constitutional flatfoot, which is a common congenital non-pathologic foot morphology. There are numerous causes of acquired adult flatfoot, including fracture or dislocation, tendon laceration, tarsal coalition, arthritis, neuroarthropathy, neurologic weakness, and iatrogenic causes. 
Causes
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is the most common cause of acquired adult flatfoot. Sometimes this can be a result of specific trauma, but usually the tendon becomes injured from wear and tear over time. This is more prevalent in individuals with an inherited flat foot but excessive weight, age, and level of activity are also contributing factors.
Symptoms
Initially, flatfoot deformity may not present with any symptoms. However, overtime as the tendon continues to function in an abnormal position, people with fallen arches will begin to have throbbing or sharp pain along the inside of the arch. Once the tendon and soft tissue around it elongates, there is no strengthening exercises or mechanism to shorten the tendon back to a normal position. Flatfoot can also occur in one or both feet. If the arch starts to slowly collapse in one foot and not the other, posterior tibial dysfunction (PTTD) is the most likely cause. People with flatfoot may only have pain with certain activities such as running or exercise in the early phase of PTTD. Pain may start from the arch and continue towards the inside part of the foot and ankle where the tendon courses from the leg. Redness, swelling and increased warmth may also occur. Later signs of PTTD include pain on the outside of the foot from the arch collapsing and impinging other joints. Arthritic symptoms such as painful, swollen joints in the foot and ankle may occur later as well due to the increased stress on the joints from working in an abnormal position for a long period of time.
Diagnosis
Starting from the knee down, check for any bowing of the tibia. A tibial varum will cause increased medial stress on the foot and ankle. This is essential to consider in surgical planning. Check the gastrocnemius muscle and Achilles complex via a straight and bent knee check for equinus. If the range of motion improves to at least neutral with bent knee testing of the Achilles complex, one may consider a gastrocnemius recession. If the Achilles complex is still tight with bent knee testing, an Achilles lengthening may be necessary. Check the posterior tibial muscle along its entire course. Palpate the muscle and observe the tendon for strength with a plantarflexion and inversion stress test. Check the flexor muscles for strength in order to see if an adequate transfer tendon is available. Check the anterior tibial tendon for size and strength.
Non surgical Treatment
Get treated early. There is no recommended home treatment. While in stage one of the deformity, rest, a cast, and anti-inflammatory therapy can help you find relief. This treatment is followed by creating custom-molded foot orthoses and orthopedic footwear. These customized items are critical in maintaining the stability of the foot and ankle. Once the tendon has stretched and deformity is visible, the chances of success for non-surgical treatment are significantly lower. In a small percentage of patients, total immobilization may arrest the progression of the deformity. A long-term brace known as an ankle foot orthosis is required to keep the deformity from progressing. The Richie Brace, a type of ankle foot orthosis, shows significant success as a treatment for stage two posterior tibial dysfunction. It is a sport-style brace connected to a custom corrected foot orthodic that fits into most lace-up footwear (including athletic shoes). It is also light weight and more cosmetically appealing than traditionally prescribed ankle foot orthosis. The Arizona Brace, California Brace or Gauntlet Brace may also be recommended depending on your needs. 
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment fails to provide relief of pain and disability then surgery is considered. Numerous factors determine whether a patient is a surgical candidate. They include age, obesity, diabetes, vascular status, and the ability to be compliant with post-operative care. Surgery usually requires a prolonged period of nonweightbearing immobilization. Total recovery ranges from 3 months to one year. Clinical, x-ray, and MRI examination are all used to select the appropriate surgical procedure.
Cause Of Acquired Flat Foot
Overview Collapsed arches occur in five percent of adults 40 years and older, especially those who are overweight or maintain sedentary lifestyles. At the onset of the condition, adult acquired flatfoot can be controlled with anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, taping, bracing, and orthotics. While most cases of adult-onset flatfoot require surgery, congenital flatfoot is an entirely different condition that is best treated with orthotics in children. Ninety percent of children born with flat feet will be fine with conservative treatment.  Causes The posterior tibial tendon, which connects the bones inside the foot to the calf, is responsible for supporting the foot during movement and holding up the arch. Gradual stretching and tearing of the posterior tibial tendon can cause failure of the ligaments in the arch. Without support, the bones in the feet fall out of normal position, rolling the foot inward. The foot's arch will collapse completely over time, resulting in adult acquired flatfoot. The ligaments and tendons holding up the arch can lose elasticity and strength as a result of aging. Obesity, diabetes, and hypertension can increase the risk of developing this condition. Adult acquired flatfoot is seen more often in women than in men and in those 40 or older. Symptoms Pain along the inside of the foot and ankle, where the tendon lies. This may or may not be associated with swelling in the area. Pain that is worse with activity. High-intensity or high-impact activities, such as running, can be very difficult. Some patients can have trouble walking or standing for a long time. Pain on the outside of the ankle. When the foot collapses, the heel bone may shift to a new position outwards. This can put pressure on the outside ankle bone. The same type of pain is found in arthritis in the back of the foot. Asymmetrical collapsing of the medial arch on the affected side. Diagnosis The diagnosis of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and AAFD is usually made from a combination of symptoms, physical exam and x-ray imaging. The location of pain, shape of the foot, flexibility of the hindfoot joints and gait all may help your physician make the diagnosis and also assess how advanced the problem is. Non surgical Treatment Nonoperative treatment of stage 1 and 2 acquired adult flatfoot deformity can be successful. General components of the treatment include the use of comfort shoes. Activity modification to avoid exacerbating activities. Weight loss if indicated. Specific components of treatment that over time can lead to marked improvement in symptoms include a high repetition, low resistance strengthening program. Appropriate bracing or a medial longitudinal arch support. If the posterior tibial tendon is intact, a series of exercises aimed at strengthening the elongated and dysfunctional tendon complex can be successful. In stage 2 deformities, this is combined with an ankle brace for a period of 2-3 months until the symptoms resolve. At this point, the patient is transitioned to an orthotic insert which may help to support the arch. In patients with stage 1 deformity it may be possible to use an arch support immediately.
Causes The posterior tibial tendon, which connects the bones inside the foot to the calf, is responsible for supporting the foot during movement and holding up the arch. Gradual stretching and tearing of the posterior tibial tendon can cause failure of the ligaments in the arch. Without support, the bones in the feet fall out of normal position, rolling the foot inward. The foot's arch will collapse completely over time, resulting in adult acquired flatfoot. The ligaments and tendons holding up the arch can lose elasticity and strength as a result of aging. Obesity, diabetes, and hypertension can increase the risk of developing this condition. Adult acquired flatfoot is seen more often in women than in men and in those 40 or older. Symptoms Pain along the inside of the foot and ankle, where the tendon lies. This may or may not be associated with swelling in the area. Pain that is worse with activity. High-intensity or high-impact activities, such as running, can be very difficult. Some patients can have trouble walking or standing for a long time. Pain on the outside of the ankle. When the foot collapses, the heel bone may shift to a new position outwards. This can put pressure on the outside ankle bone. The same type of pain is found in arthritis in the back of the foot. Asymmetrical collapsing of the medial arch on the affected side. Diagnosis The diagnosis of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and AAFD is usually made from a combination of symptoms, physical exam and x-ray imaging. The location of pain, shape of the foot, flexibility of the hindfoot joints and gait all may help your physician make the diagnosis and also assess how advanced the problem is. Non surgical Treatment Nonoperative treatment of stage 1 and 2 acquired adult flatfoot deformity can be successful. General components of the treatment include the use of comfort shoes. Activity modification to avoid exacerbating activities. Weight loss if indicated. Specific components of treatment that over time can lead to marked improvement in symptoms include a high repetition, low resistance strengthening program. Appropriate bracing or a medial longitudinal arch support. If the posterior tibial tendon is intact, a series of exercises aimed at strengthening the elongated and dysfunctional tendon complex can be successful. In stage 2 deformities, this is combined with an ankle brace for a period of 2-3 months until the symptoms resolve. At this point, the patient is transitioned to an orthotic insert which may help to support the arch. In patients with stage 1 deformity it may be possible to use an arch support immediately.  Surgical Treatment If conservative treatment fails to provide relief of pain and disability then surgery is considered. Numerous factors determine whether a patient is a surgical candidate. They include age, obesity, diabetes, vascular status, and the ability to be compliant with post-operative care. Surgery usually requires a prolonged period of nonweightbearing immobilization. Total recovery ranges from 3 months to one year. Clinical, x-ray, and MRI examination are all used to select the appropriate surgical procedure.
Surgical Treatment If conservative treatment fails to provide relief of pain and disability then surgery is considered. Numerous factors determine whether a patient is a surgical candidate. They include age, obesity, diabetes, vascular status, and the ability to be compliant with post-operative care. Surgery usually requires a prolonged period of nonweightbearing immobilization. Total recovery ranges from 3 months to one year. Clinical, x-ray, and MRI examination are all used to select the appropriate surgical procedure.